1.
Preparation
This is the effect we are going to make in this tutorial.
Note: The main content of this tutorial comes from the
Tip: Use ⬆️ ⬇️ to turn the page up and down. We recommend browsing with a large screen for a better reading experience.
Note: The main content of this tutorial comes from the
Content Examples that come with Unreal EngineTip: Use ⬆️ ⬇️ to turn the page up and down. We recommend browsing with a large screen for a better reading experience.

Full Tutorials:
1. UE Niagara: Simple Sprite Emitter
2. UE Niagara: Simple Mesh Emitter
3. UE Niagara: Simple GPU Emitter
4. UE Niagara: Sprite Facing
5. UE Niagara: Blend Attributes By Value
6. UE Niagara: Static Beams
7. UE Niagara: Dynamic Beams
8. UE Niagara: Multiple Renderers
9. UE Niagara: Location Events
10. UE Niagara: Expressions
1. UE Niagara: Simple Sprite Emitter
2. UE Niagara: Simple Mesh Emitter
3. UE Niagara: Simple GPU Emitter
4. UE Niagara: Sprite Facing
5. UE Niagara: Blend Attributes By Value
6. UE Niagara: Static Beams
7. UE Niagara: Dynamic Beams
8. UE Niagara: Multiple Renderers
9. UE Niagara: Location Events
10. UE Niagara: Expressions

3.
Introduction
Collision queries are done with either line traces on the cpu or depth buffer/distance field checks on the gpu. the query results are saved and can also be used by subsequent modules.
This example shows a collision event being sent to a different emitter which spawns particles in response to that event.
This example shows a collision event being sent to a different emitter which spawns particles in response to that event.

4.
Introduction
Collisions can optionally generate events using the "Generate Collision Event" module. These are only supported on the CPU.
Collisions work on both CPU and GPU emitters, though some options are different. For instance, only GPU emitters can sample the scene depth, or the global distance field.
CPU Collisions are quite expensive compared to GPU collisions, generally, and should be used sparingly.
Collisions work on both CPU and GPU emitters, though some options are different. For instance, only GPU emitters can sample the scene depth, or the global distance field.
CPU Collisions are quite expensive compared to GPU collisions, generally, and should be used sparingly.

5.
Let's start the reconstruction
Right click and select
FX => Niagara System to create. 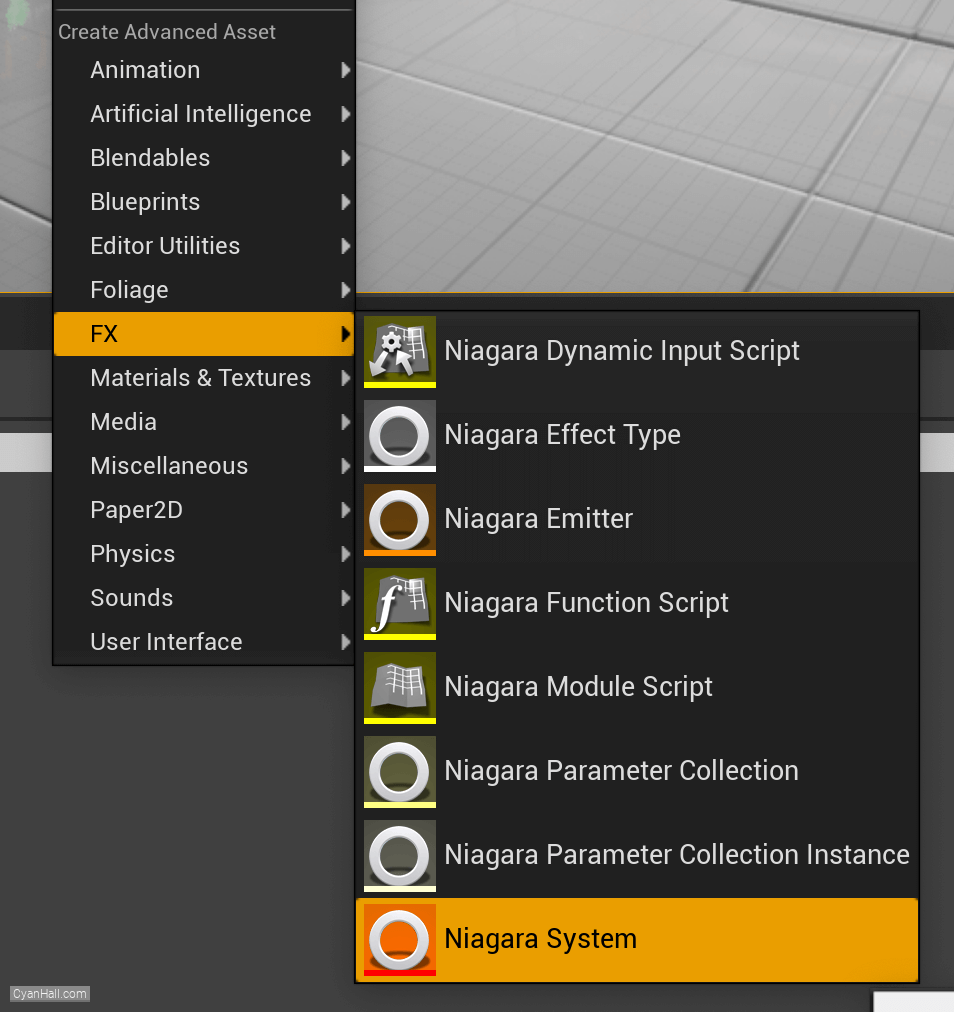
6.
Create Niagara System
Select
Empty template, click + three times and click Finish 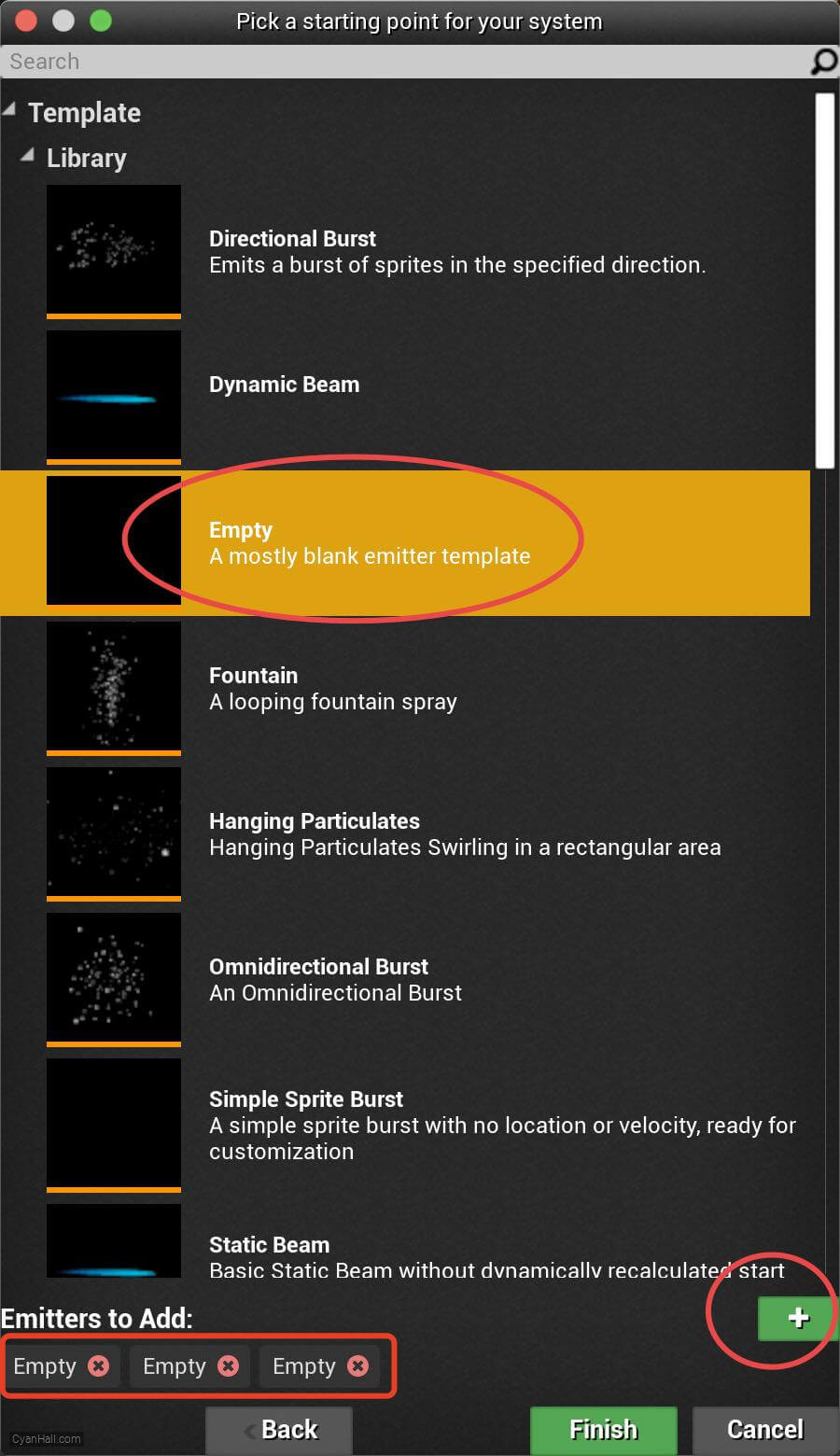
7.
Create Niagara System
As a result, we get a
Niagara System asset, click to open it. 
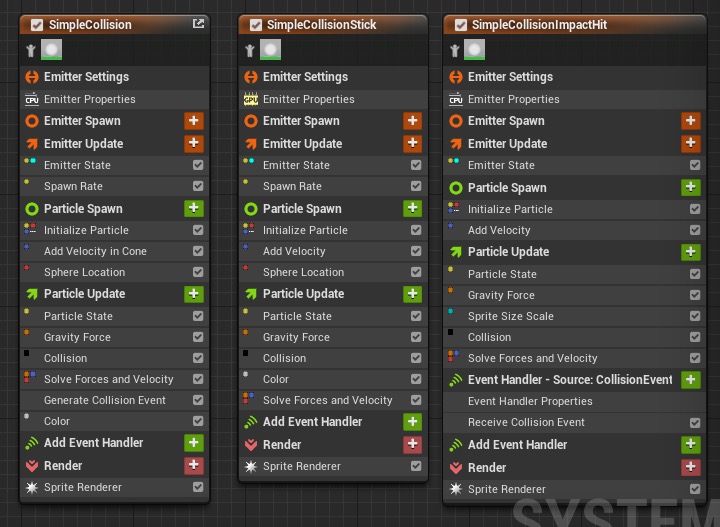
8.
Three Emitters
You can see that we have three emitters, renaming them
CollisionGen generates events, CollisionStick generates ribbon particles based on events, and CollisionImpactHit generates sprite particles based on events.
CollisionGen, CollisionStick, and CollisionImpactHit, respectively.CollisionGen generates events, CollisionStick generates ribbon particles based on events, and CollisionImpactHit generates sprite particles based on events.
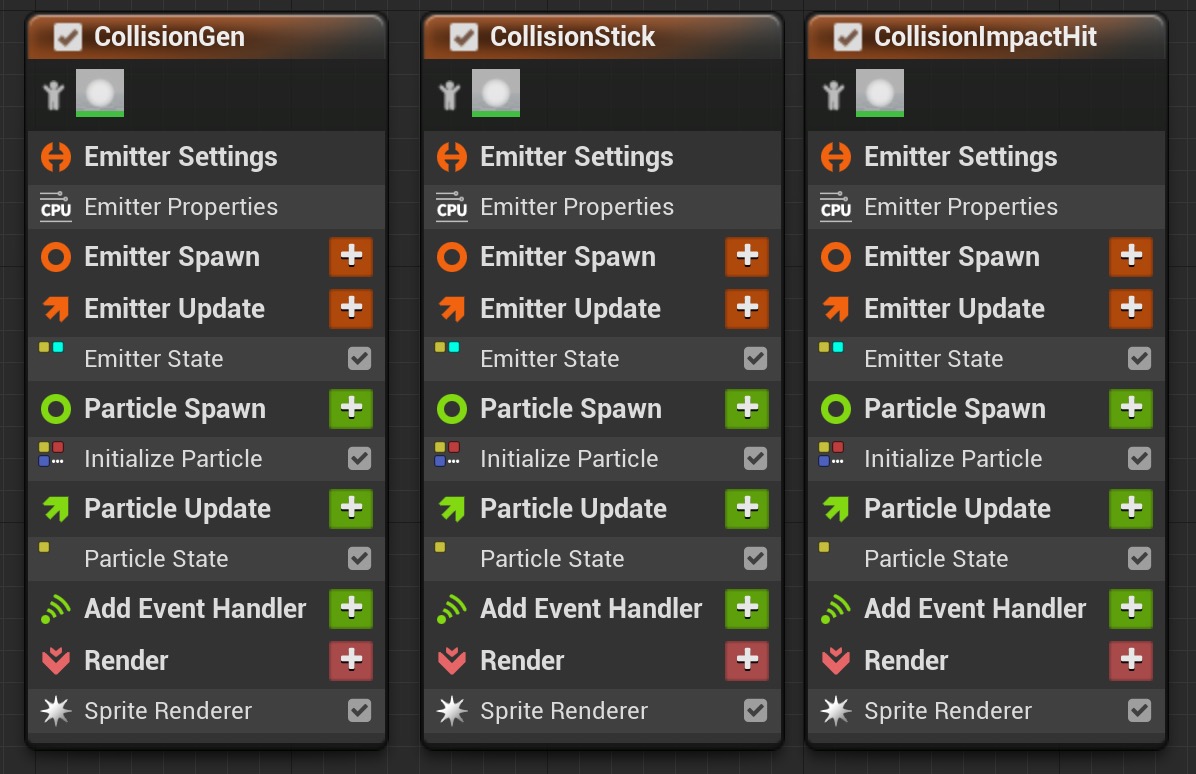
9.
Three Emitters
First, work on the CollisionGen stack.


10.
Spawn Rate
Click on the
+ sign to the right of the Emitter Update to add the Spawn Rate module.Spawn Rate: Number of particles per second to spawn. 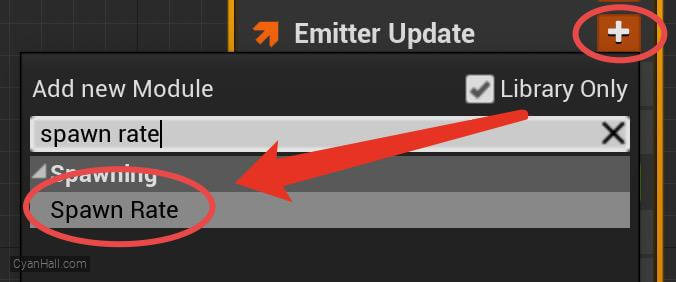
11.
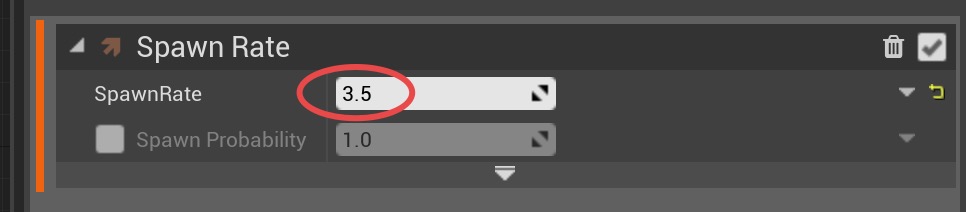
Spawn Rate
Set the
Spawn 3.5 particle per second.
Spawn Rate value to 3.5.Spawn 3.5 particle per second.
12.
Initialize Particles
Select
1.
2.
3.
Initialize Particles and set:1.
Lifetime is 7.02.
Color Mode is Direct Set3.
Sprite Size Mode is Uniform and has a value of 14.0 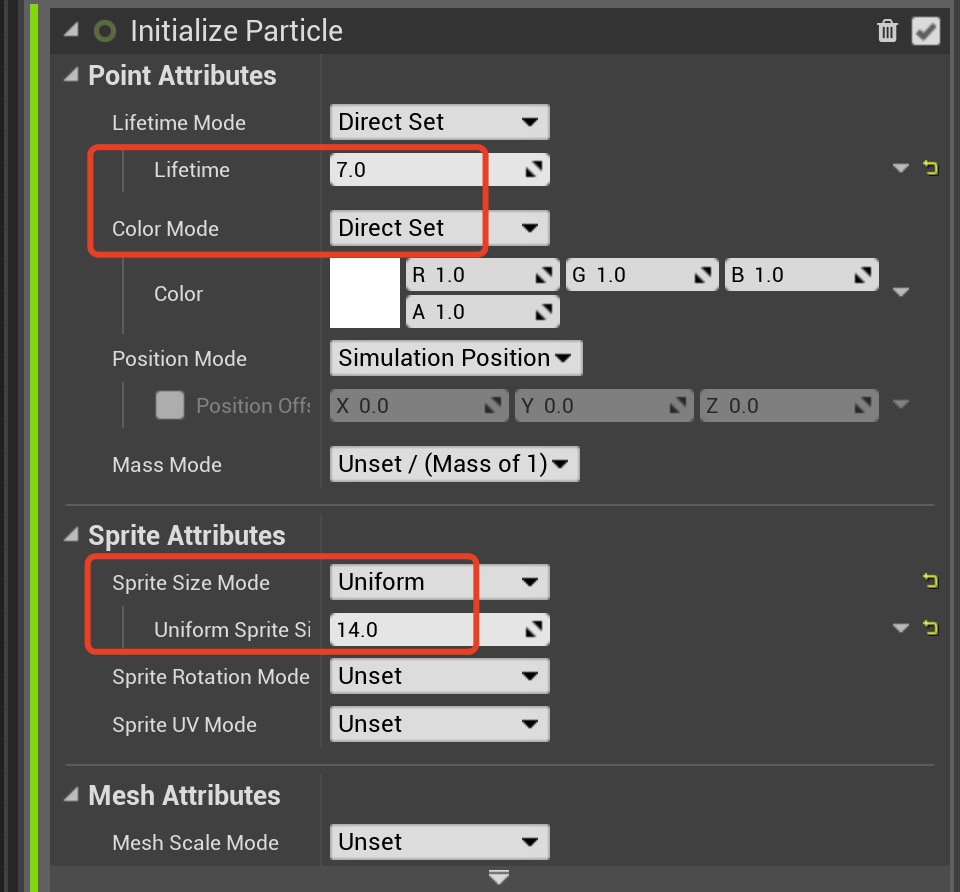
13.
Add Velocity in Cone
Add
Add Velocity in Cone module to the Particle Spawn section. 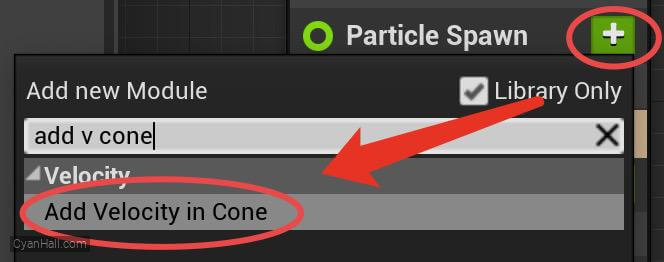
14.
Add Velocity in Cone
Click the first
Fix issue button to add its dependency on the SolveForcesAndVelocity module. 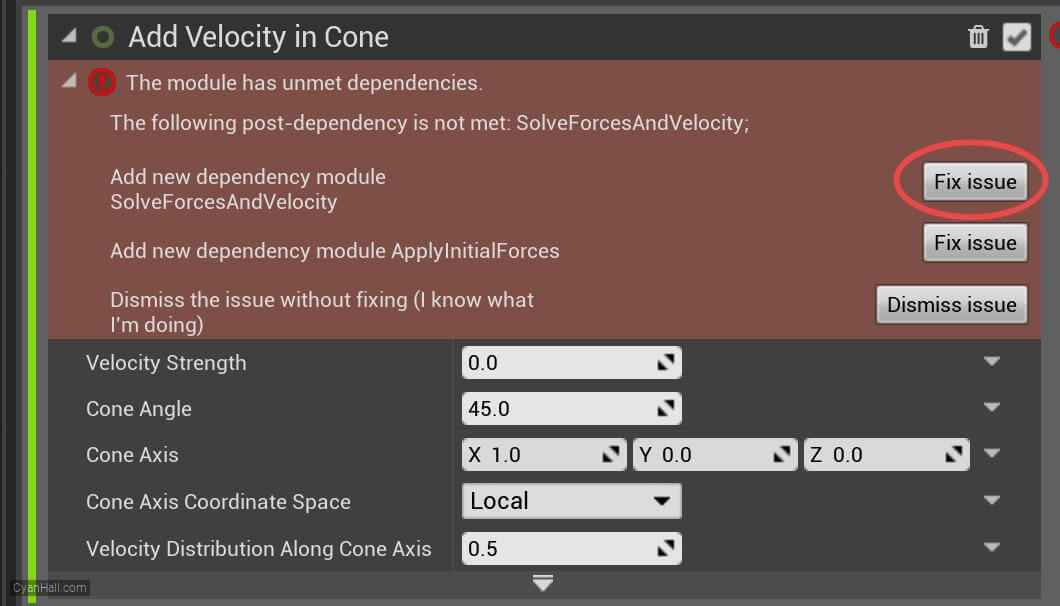
15.
Add Velocity in Cone
Set the value type of
Velocity Strength to Random Range Float 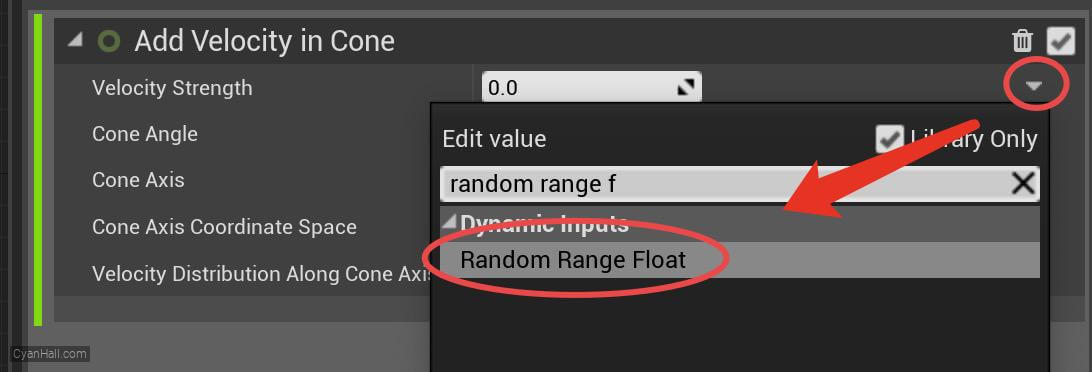
16.
Add Velocity in Cone
1. Set Velocity Strength to a minimum value of
2. Set the Cone Angle to
3. Set the Cone Axis to
250.0 and a maximum value of 750.0.2. Set the Cone Angle to
24.0.3. Set the Cone Axis to
(0, 0, 1). 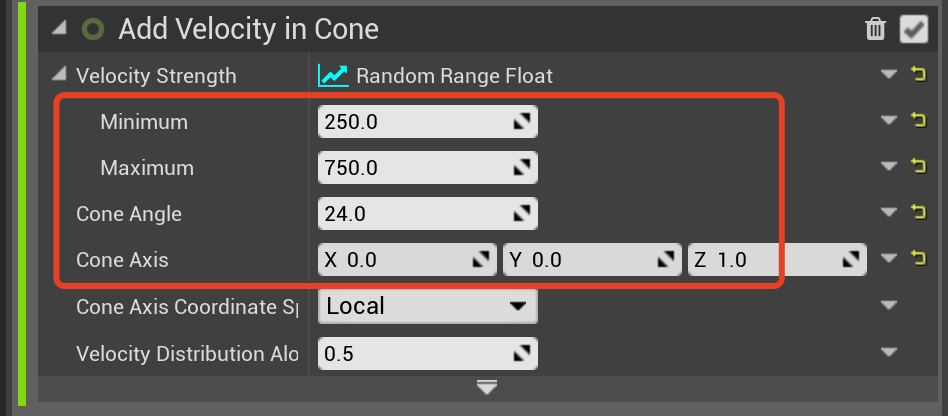
17.
Sphere Location
Add the
Sphere Location module in the Particles Spawn section. 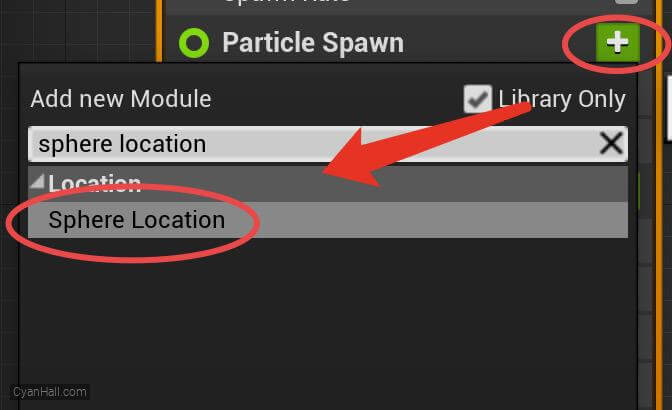
18.
Sphere Radius
Set
Sphere Radius to 10.0 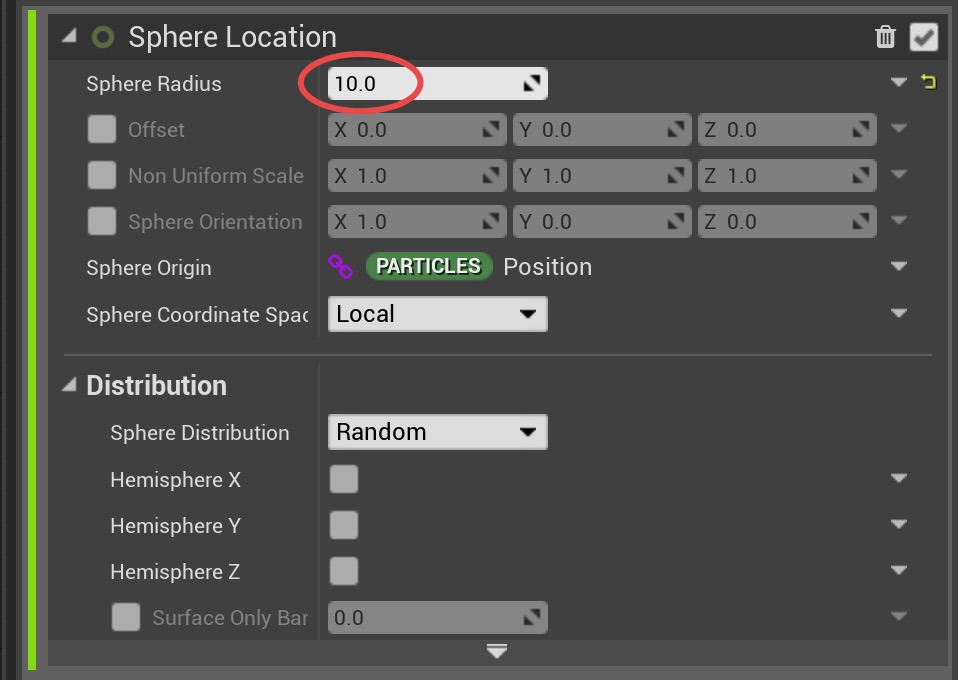
19.
Collision
Add
Add Velocity in Cone module to the Particle Spawn section. 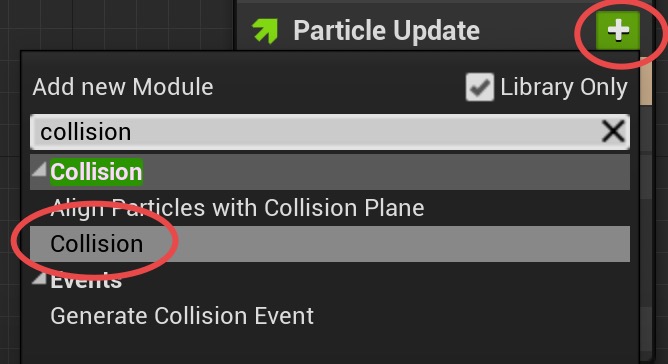
20.
Collision
Click the first
Fix issue button to fix the SolveForcesAndVelocity module's dependency order issue. 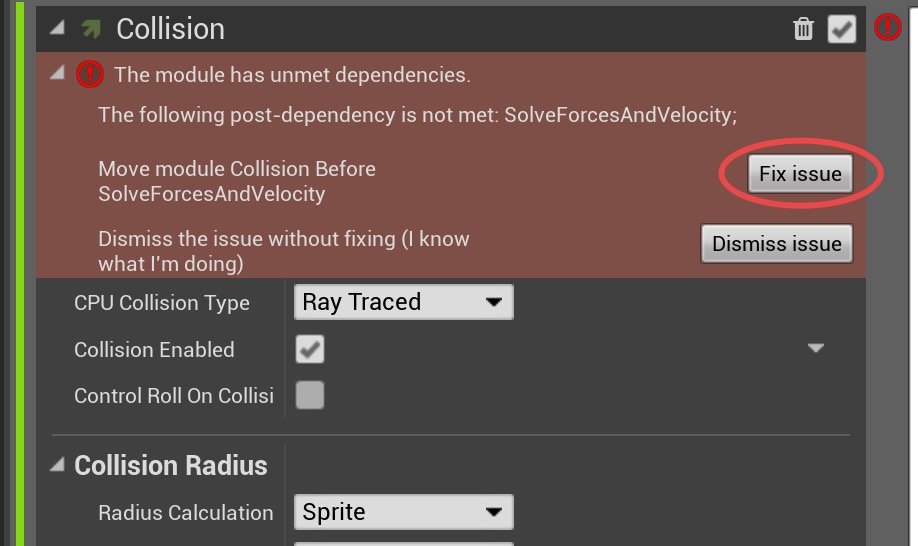
21.
Collision
Set
Restitution Coefficient Blending to Min 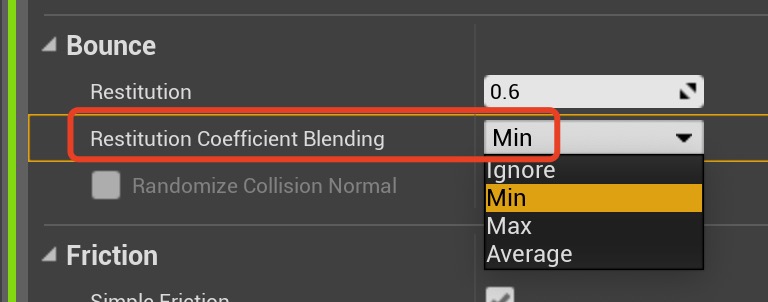
22.
Persistent IDs
Check
Requires Persistent IDs to obtain persistent IDs so that the generated events can be received by other emitters. 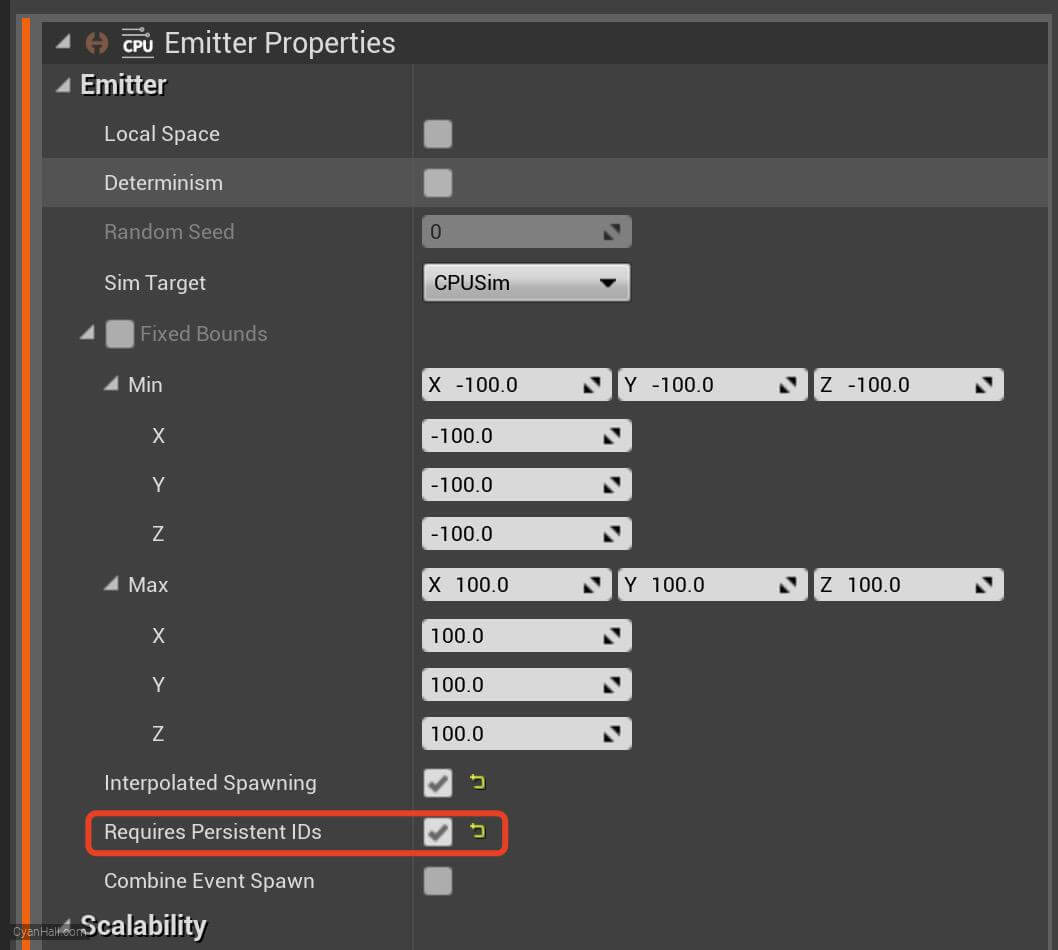
23.
🎉 Finish! 🎉
👉  Star me if it’s helpful.
Star me if it’s helpful.
Support Me: Patreon
Follow Me: Twitter, Reddit, Zhihu, Bilibili
Support Me: Patreon
Follow Me: Twitter, Reddit, Zhihu, Bilibili